Malware: Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malicious code with the ability to hijack data from information systems through state-of-the-art cryptographic encryption.
At DarkData, we specialize in the prevention and mitigation of ransomware attacks.

Information about Ransomware
A ransomware attack is typically deployed through an email attachment, which can be an executable, a file, or an image. Once the attachment is opened, the malware deploys in the user’s system. Cybercriminals can also hide the malware on web pages, infecting visitors’ devices without their knowledge.
The infection is not immediately evident to the user. The malware operates stealthily in the background until a data locking system or mechanism is triggered. Then a dialog window appears informing the user that the data has been locked and requesting a ransom to unlock it. At that point, it’s too late to save the data through security measures
Any user or business can be a victim of ransomware. Cybercriminals are not selective and often seek to infect as many users as possible to maximize their income.
Yes, because cybercriminals know that organizations are more likely to pay due to the fact that the affected data is often more sensitive and vital for their continuity. Additionally, sometimes it may be more expensive to restore the data through backups than to pay the ransom.
In some cases, yes. It is possible in the following cases:
- The malware authors made implementation errors, making it possible to break the encryption. This was the case with the well-known ransomware Petya and CryptXXX, for example.
- Keys are leaked, or a master key, as in the case of TeslaCrypt.
- Authorities seize servers with keys and share them with the cybersecurity community. An example is CoinVault.
Paying ransoms is not advisable, but mostly for large companies, it is the only solution. These are cases where there are no backups, and every hour of business continuity loss translates into millions of monetary losses.
In this case, it is recommended to use ransomware negotiation services like those provided by DarkData; where adversaries are meticulously studied to ensure that payments result in recovered information.
It is not recommended to pay the ransom under any circumstances, mainly because it does not guarantee a solution to the problem. For example, there may be errors in the malware that prevent the encrypted data from being recovered even with the correct key.
In the case of a ransomware problem, there are multiple possible solutions. Contact DarkData and we will advise you.
Ransomware Characteristics
There are hundreds of different families of ransomware malware currently. Additionally, some old families are becoming active again due to code modifications made by various criminal groups. Ransomware exists for Microsoft, GNU/Linux, and MAC OS X operating systems, as well as for mobile devices.
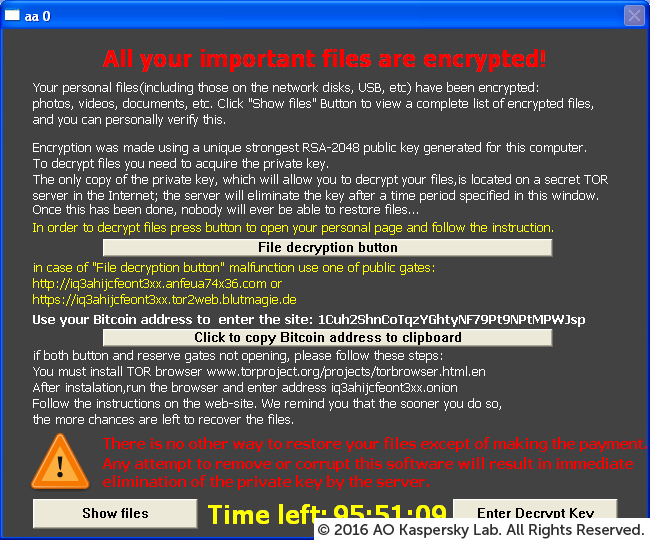
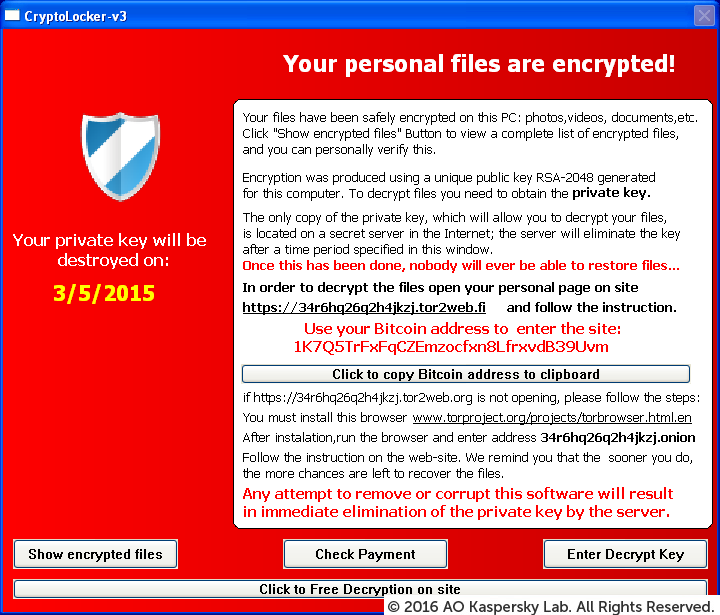
Types of Malware
According to the mode of affecting the target system and its characteristics.
Encryption Ransomware
Encrypts files and folders. The original files are deleted after encryption. A lock screen is usually displayed.
Lock Screen Ransomware
System Lock Screen: Affects the system’s screen and displays a payment request. It usually does not encrypt files or folders.
Master Boot Record (MBR) Ransomware
This type of ransomware modifies the system’s Master Boot Record (MBR) to interrupt the system boot.
Mobile Ransomware
It mainly affects the Android operating system. The infection usually originates from downloads of applications from unofficial Android markets.